#1 Stop any command mid-operation
Since you might be testing some commands... pressing Ctrl + C will cancel a command that you've already entered and allow you to begin typing another one, while typing cls will clear the current window of any commands that you've entered.
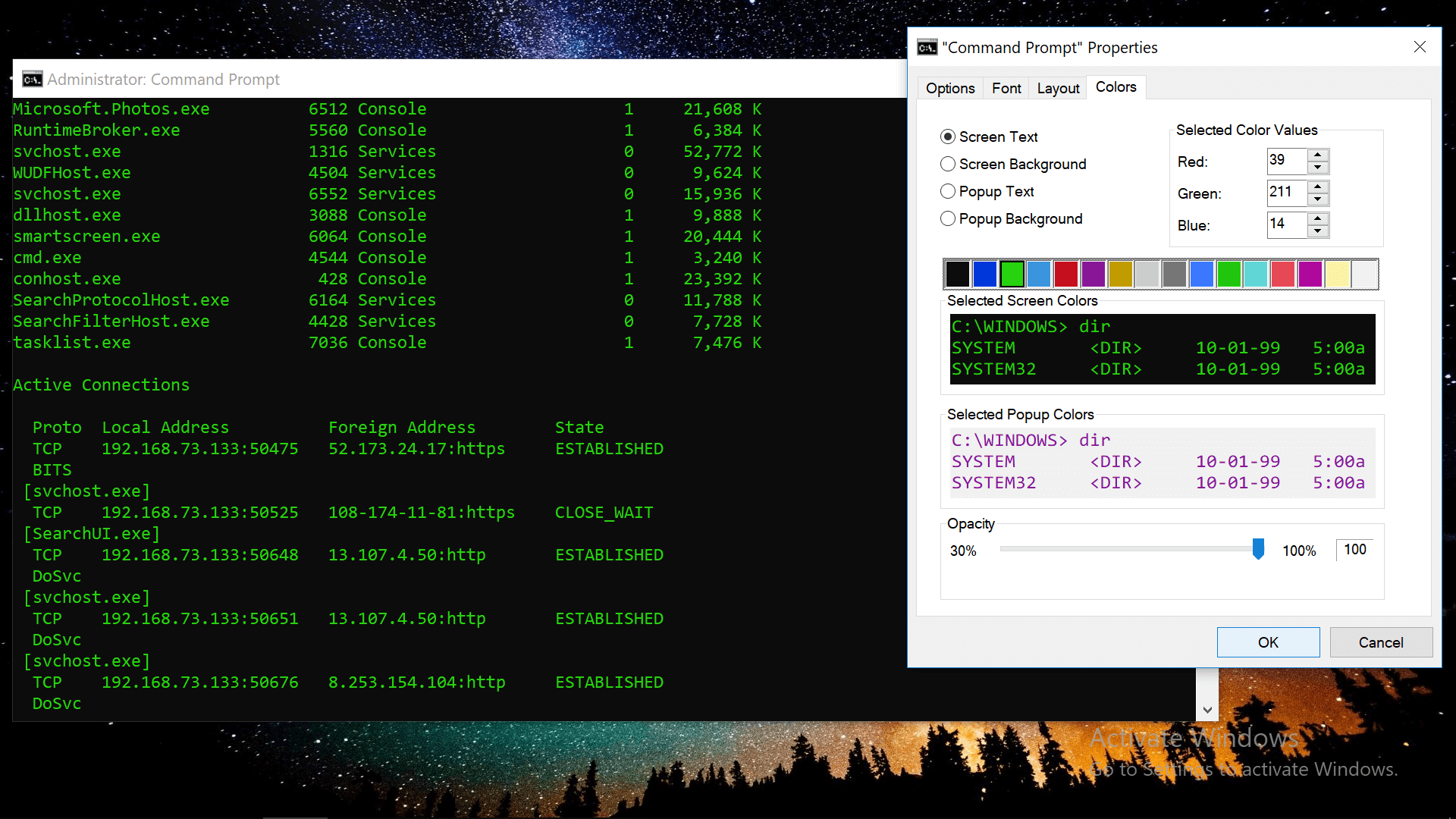
#2 Did you know there is a settings menu?
Right-click the title bar and open Properties for settings that include the ability to change your Command Prompt's font, layout and colors, as well as options such as Quick Edit mode, which will automatically paste text from your clipboard when you right click in the window.
Bonus: You can customize the text in the top bar by typing title followed by the text that you want (example: title My title was pasted with Quick Edit mode).
#3 Command Prompt keyboard shortcuts
Tapping the up and down arrows on your keyboard will cycle through commands that you've previously entered. More shortcuts:
Tab: When you're typing a folder path, tab will auto-complete and cycle through directories
Ctrl + M: Enables Mark Mode which lets you move the cursor in all directions with the arrow keys
Ctrl + C or V: As of Windows 10, you can copy and paste with control C and V like elsewhere around the OS
Ctrl + F: Likewise, control + F now lets you search for text in the Command Prompt
Ctrl + Shift + Scroll on your mouse: Increases or decreases the window transparency (+ and - keys work too)
Alt + Enter: Enables full-screen mode with no title bar displayed on top (F11 also works like elsewhere in Windows)
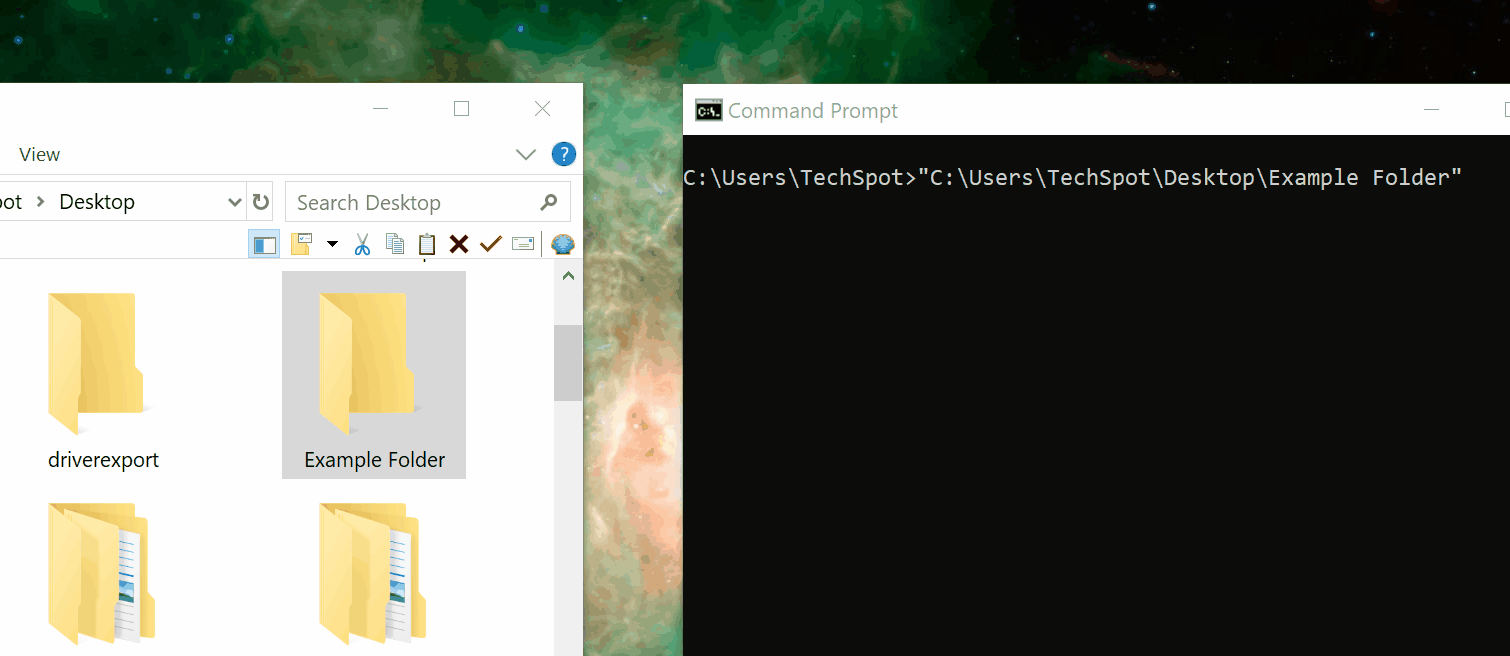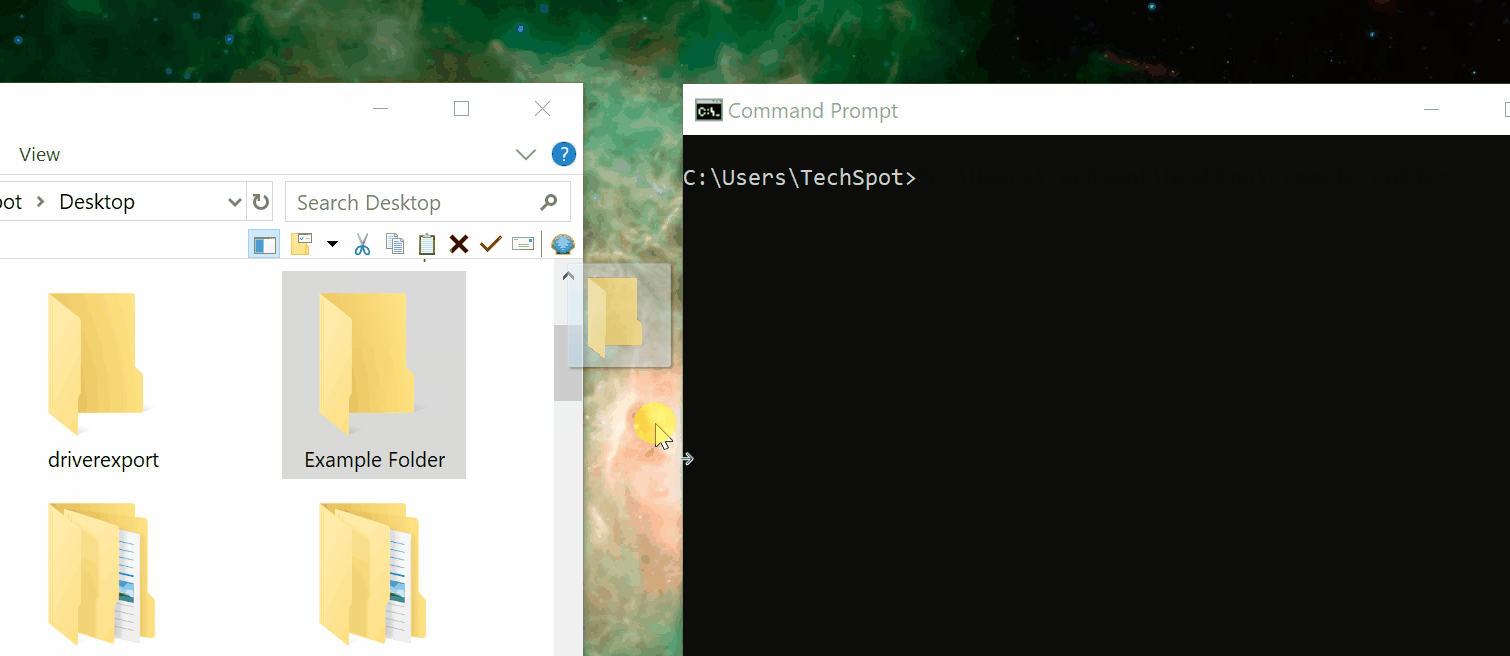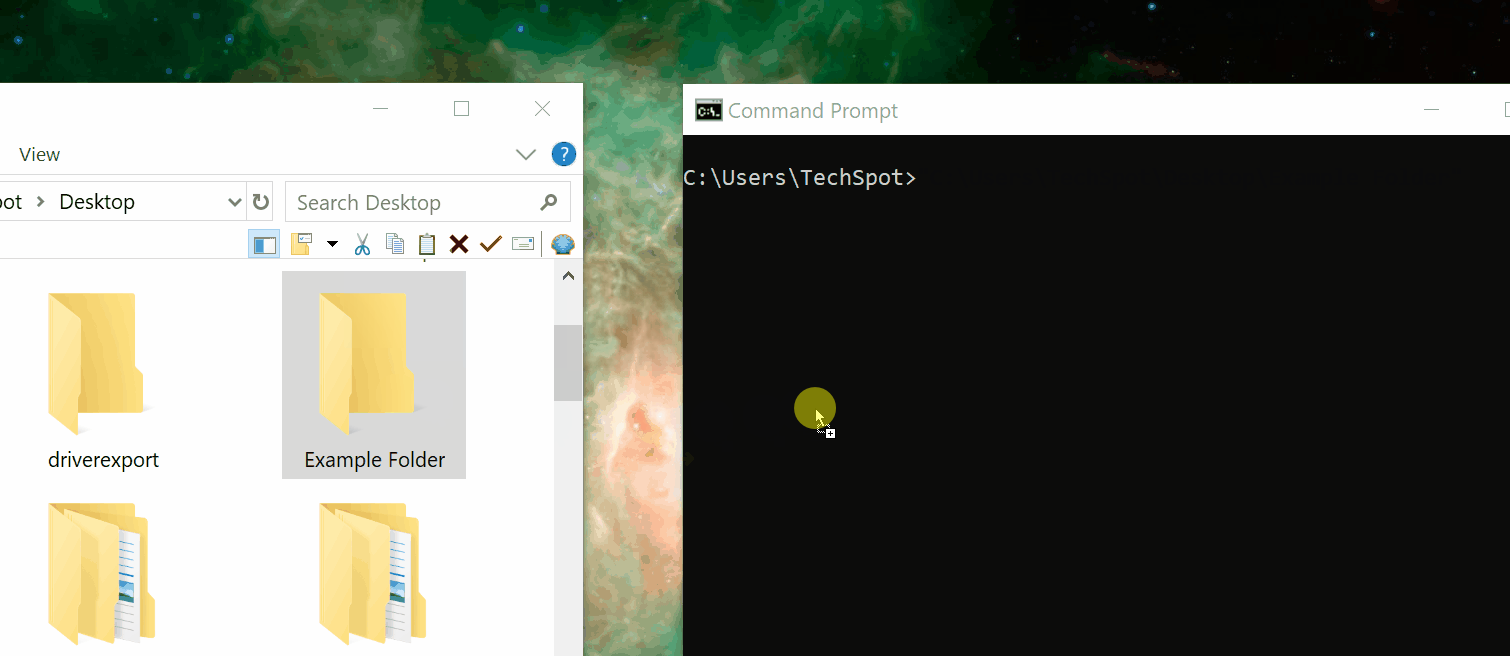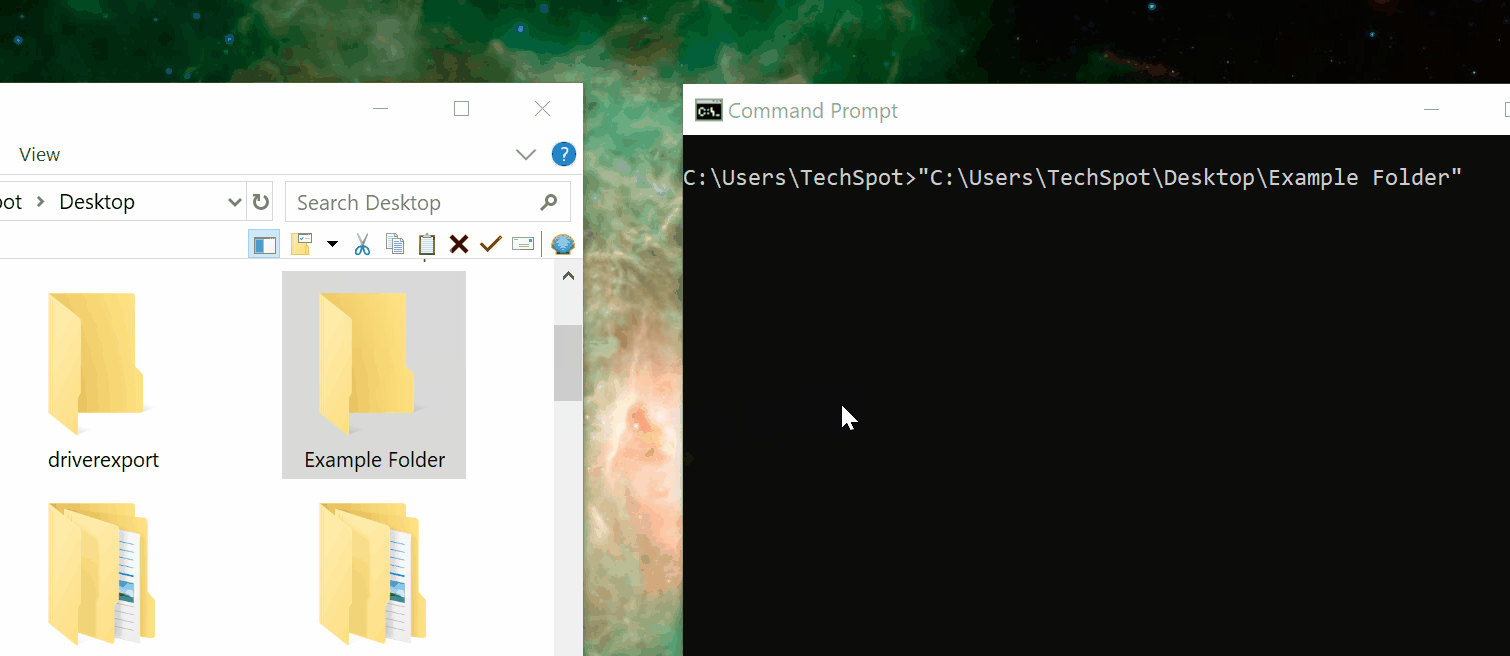
Drag and drop folders to insert a directory path
Directory paths don't have to be typed in the first place. Aside from being able to copy/paste text and tab through directories, you can drag and drop a folder directly into the Command Prompt window to automatically insert the location.
#3 The function keys F1-F9 are also shortcuts
The function (F) keys on the top of your keyboard are also shortcuts that mostly re-enter previous commands without retyping them.
- F1: Tapping or holding this key will retype the command that you just entered letter by letter.
- F2: Copies the current command up to a specified character.
- F3: Completely retypes the previous line that you entered.
- F4: The reverse of F2 -- auto-deletes up to a specified character (your cursor must be in front of the text).
- F5: Retypes the previous command like F3 but lets you cycle back through many lines in your command history.
- F6: Inserts Ctrl+Z (^Z) in the Command Prompt, which is an end-of-file indication (text after this is ignored)
- F7: Opens a list of previously entered commands that you can select from.
- F8: Works like F5 but doesn't stop at the end of your command history, cycles back to the start.
- F9: Lets you retype a previous command by entering a number associated with the line.
#4 Enter multiple commands at once
Adding && between commands will let you enter multiple lines at once to be executed in succession. Example:
tasklist && netstat -b
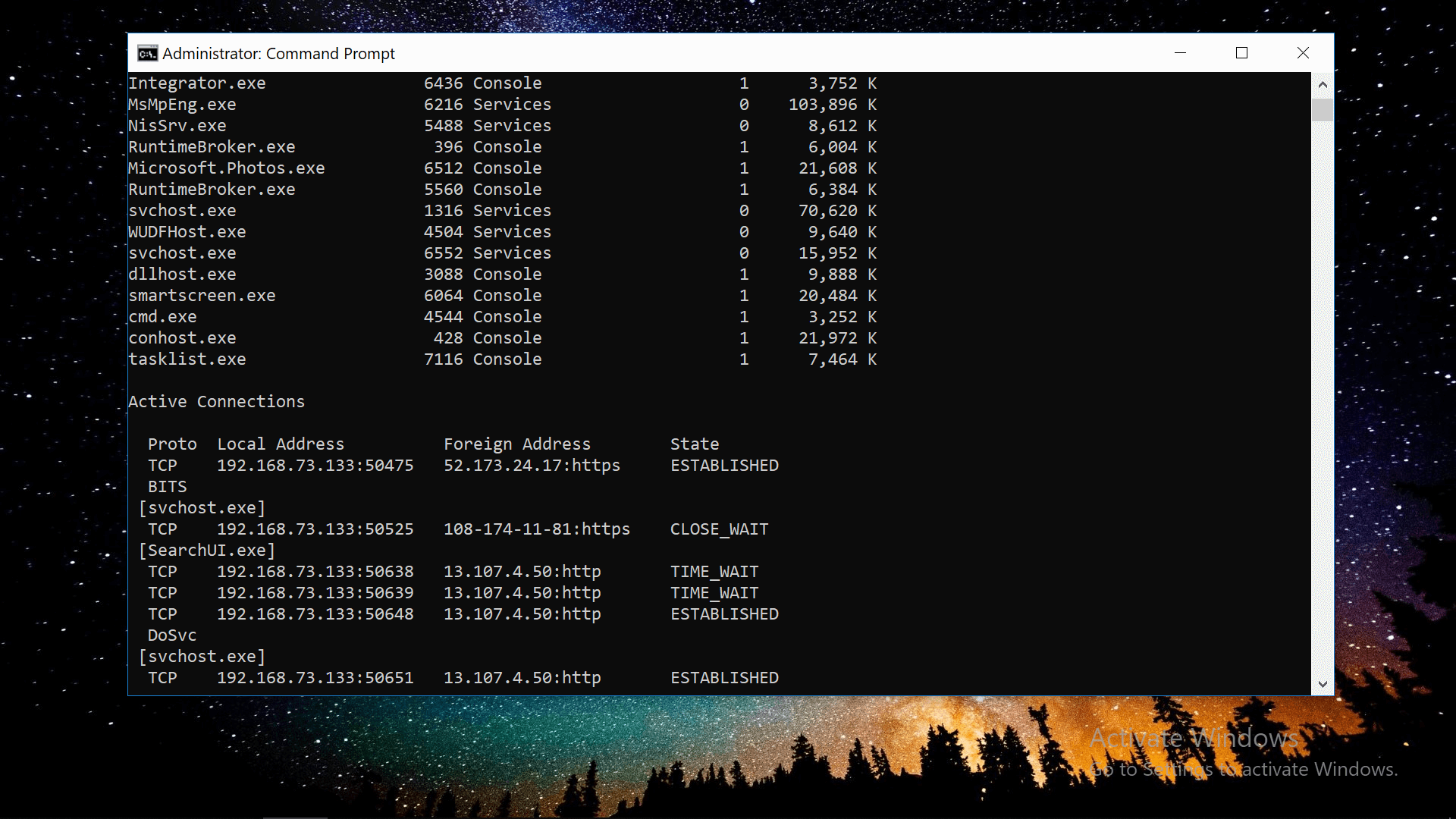
#5 See every process running and connected
Entering tasklist command will list all of the processes running on your machine along with details such as their process identifier and memory usage, while netstat -b will generate a list of all the processes with an established network connection.
#6 List every device driver on your PC
There are many ways to generate a list of drivers in the Command Prompt, here's one line that includes additional information such as the status of a device and the folder location/file name of the associated driver:
driverquery /FO list /v
#7 Output results to text file or clipboard
You can save the output of a command such as tasklist or driverquery to a new text file by adding > along with a directory and file name. Example:
driverquery > C:\Users\TechSpot\Desktop\output.txt
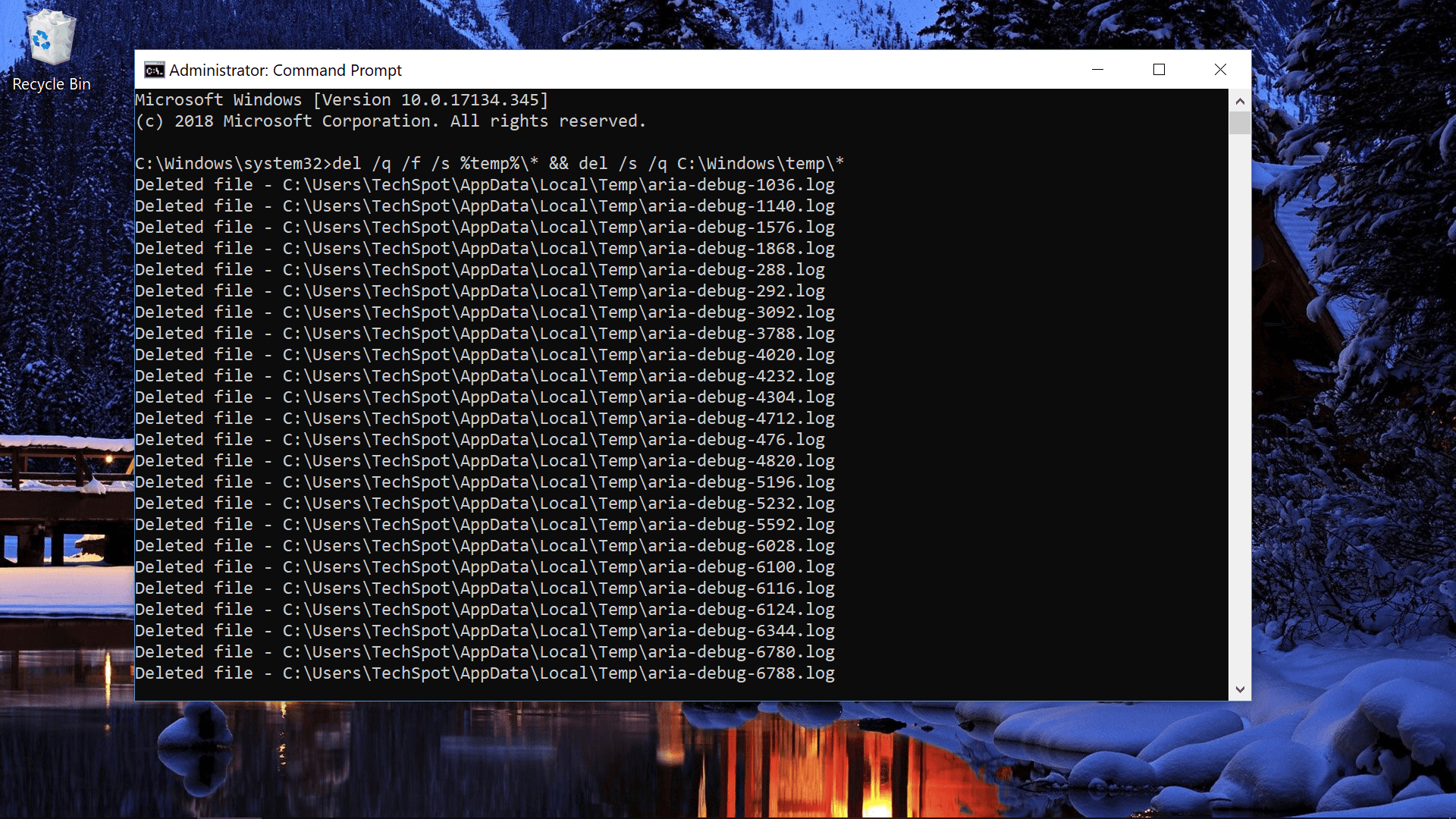
#8 Delete temporary files from your drive
Some of the temporary files on your drive can be deleted with the following commands (/q runs the operation without a confirmation prompt, /f ignores the read-only attribute and forces deletion, /s deletes contents from all sub-folders):
- Delete temporary user files: del /q /f /s %temp%\*
- Delete temporary system files (requires admin rights): del /s /q C:\Windows\temp\*
- ...Or run them together: del /q /f /s %temp%\* && del /s /q C:\Windows\temp\*
If that didn't empty enough storage, here are more temp folder locations, and we recently covered a bunch of ways to free up space on Windows, including Command Prompt methods to launch an advanced Disk Cleanup tool and another to disable hibernation by deleting the feature's system file (hiberfil.sys).
#9 Open Windows' on-screen keyboard
Entering osk into a Command Prompt opens Windows' on-screen keyboard which lets you click keys with your mouse instead of typing them.
#10 Shutdown your PC at a certain time
The "shutdown" command can be used with a range of switches to shutdown, reboot and more, including the ability to force applications closed, to display a message on shutdown, and to specify the number of seconds you'd like before the operation happens. Example: shutdown -s -t 3600 would shutdown your PC in one hour.
Comments
Post a Comment